DON’T HAVE INTERCOURSE FROM A WEEK AFTER YOUR OVULATION.

For couples trying to conceive, timing of intercourse plays a significant role. Ovulation usually occurs around the mid-cycle, typically between day 10 and day 14 of a regular menstrual cycle. This is the most fertile window, and couples are generally advised to have intercourse during this period to maximize the chances of conception. After ovulation, the luteal phase begins. During this phase, the fertilized egg, if conception has occurred it travels to the uterus for implantation. At this point, excessive or poorly timed intercourse does not enhance conception and, in some cases, may interfere with implantation. Healthcare professionals often advise moderation after ovulation, allowing the body to support early implantation and stable hormone balance. Always consult your fertility specialist for personalized guidance, as recommendations may vary based on individual medical history and fertility treatment plans.
FIBROID COULD PREVENT YOU FROM GETTING PREGNANT.
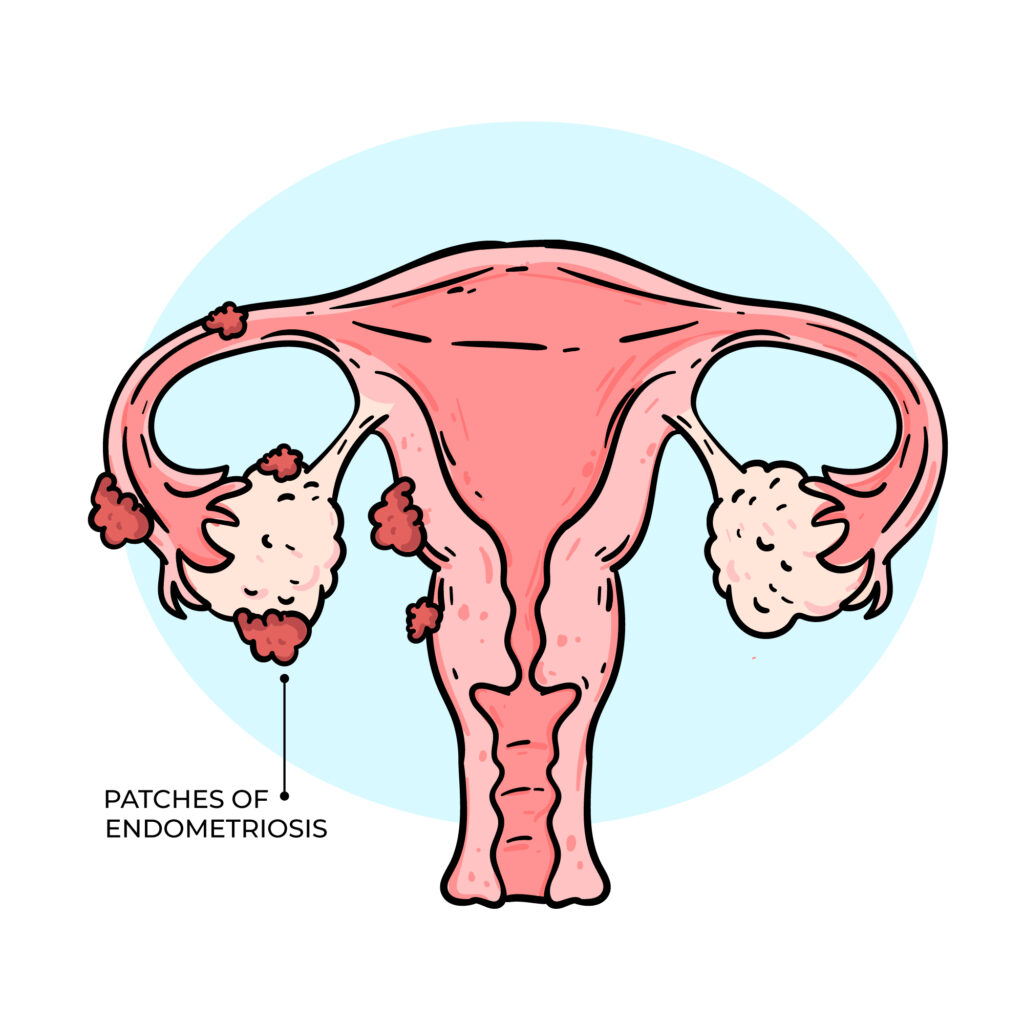
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that can affect a woman’s ability to conceive, depending on their size, number, and location. Certain types of fibroids, especially those that distort the uterine cavity (submucosal fibroids), may interfere with blood supply and nutrient flow to the endometrium, thereby affecting implantation and pregnancy. While some fibroids may not significantly impact fertility, others can pose challenges. The main ways fibroids may affect conception include: 1. Reduced implantation potential Fibroids that distort the uterine cavity can decrease the ability of the embryo to successfully implant, even when they are relatively small. 2. Hormonal influence Some fibroids may alter the local hormonal environment of the uterus, affecting fertility. Research suggests that fibroids can influence the balance of reproductive hormones, potentially reducing the likelihood of pregnancy. 3. Uterine contractility Normal uterine contractility gentle wave-like movements of the uterus helps facilitate embryo implantation and early pregnancy development. Fibroids can disrupt this process, making it more difficult for the uterus to support a pregnancy. For these reasons, fibroids should not be dismissed as harmless in women who are experiencing infertility or recurrent pregnancy loss. A thorough evaluation is recommended to determine whether fibroids may be contributing to fertility challenges and to guide appropriate management.
CAN HORMONAL TESTS BE DONE AT ANY TIME DURING THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE?

Traditionally, hormonal tests such as Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH) are performed on day 2 or day 3 of the menstrual cycle. The reason is that, at this stage, these hormones are usually at a stable baseline, making it possible to assess ovarian reserve more accurately. However, with the advancement of reproductive medicine, Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) testing has become the gold standard for evaluating ovarian reserve. Unlike FSH and LH, AMH can be measured at any point in the menstrual cycle, as its levels remain relatively stable throughout. AMH provides a more sensitive and reliable indication of the remaining egg supply and overall ovarian function. It is important to understand that the menstrual cycle is divided into three phases: Follicular Phase (menstrual bleeding to ovulation) Ovulatory Phase (release of the egg) Luteal Phase (post-ovulation until the next cycle begins) A professional who understands these phases and the dynamics of reproductive hormones will be able to determine which tests are cycle-dependent (like FSH and LH) and which are cycle-independent (like AMH).
OVARIAN REJUVENATION

IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR WOMEN WITH LOW OVARIAN RESERVE This is for women who have been diagnosed with low ovarian reserve, premature ovarian insufficiency, or chronic PCOS, and are exploring options to conceive using their own eggs. The desire to conceive with one’s own eggs is completely valid and deeply personal. However, when ovarian reserve is diminished or absent, options become more limited. One experimental approach currently being explored is known as ovarian rejuvenation. Ovarian rejuvenation refers to a research-based, experimental procedure aimed at stimulating or restoring ovarian function in women with low or absent egg reserves. It is hypothesized to potentially reactivate dormant or aging ovarian tissue, possibly leading to the production of viable eggs. However, it is important to note that this treatment is not yet proven, and its efficacy and safety have not been fully established in large-scale clinical studies. There are three proposed methods of ovarian rejuvenation: 1. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy – Involves injecting PRP directly into the ovaries. It is thought to help stimulate follicle development and improve ovarian function. This is currently the most commonly used technique in countries like Nigeria. 2. Stem Cell Therapy – Involves the use of stem cells (often from the patient’s own bone marrow or adipose tissue) to potentially regenerate ovarian tissue. 3. In vitro Activation – This involves using certain agents or compounds to trigger dormant follicles to resume growth. Before considering any form of ovarian rejuvenation, it is essential to: Undergo a full reproductive hormone panel, including Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) testing, to assess your current ovarian reserve. Consult with a board-certified fertility specialist Patients should be fully informed and cautious, as many clinics may offer these services without sufficient scientific backing or regulatory approval. Final Thoughts: While the idea of ovarian rejuvenation offers hope, it is important not to make decisions based on hype or pressure. Always seek evidence-based advice from qualified medical professionals, and remember that this approach remains investigational at this time.
Uterine Cramping After Ovulation

Experiencing uterine cramps after ovulation, either continuously until your next menstrual period or several days after ovulation, may be linked to different underlying causes. Two common possibilities include: 1. Incomplete Follicular Maturation or Follicular Persistence In some cases, ultrasound reports may show the presence of dominant follicles; however, some follicles may not have matured fully or may fail to rupture. When eggs do not reach maturity or are not released, these persistent follicles can lead to the formation of ovarian cysts. This process may trigger pelvic discomfort or cramping after ovulation. 2. Progesterone Insufficiency or Impaired Endometrial Response After ovulation, progesterone plays a key role in preparing the uterine lining (endometrium) for implantation. Low progesterone levels can cause uterine contractions or cramping due to inadequate support for implantation. In some cases, a woman may have normal progesterone levels, but the endometrium may not respond effectively to the hormone—a condition sometimes referred to as reduced endometrial receptivity. Why Evaluation is Important If you experience persistent cramping after ovulation, it is important to consult a qualified healthcare professional. Hormonal evaluation, pelvic ultrasound, and endometrial receptivity assessment may be required to identify the cause. Addressing hormonal imbalance, improving follicular development, and enhancing endometrial receptivity can increase the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
WHEN YOU PERIOD BECOMES IRREGULAR BECAUSE OF FERTILITY TREATMENT

Some women do complain that their period become irregular as soon as they place them on fertility treatment. It is possible that you may be menstruating regularly and your body may be good yet not get pregnant. two things are likely to be the problem that makes your period to stop or scanty, it may be due to low quality of egg which means you have PCOS. It is because your body sensed the change in your body due to the treatment and was fighting it due to your age. The Second, is that if you have PCOS and you take any treatment that will make you to ovulate, the egg might be seen at the mid-cycle but stopped your period at the end of the cycle because your body failed to respond positively to the treatment being given to you. My advice is to visit a fertility clinic for evaluation an to know what to do.
WHEN YOU SPOT OR BLEED WHEN YOU HAVE INTERCOURSE WITH YOUR HUSBAND.
If you notice spotting or bleeding after sexual intercourse, especially a few days after your menstrual period, it may be due to several possible causes. These include hormonal imbalances, cervical or uterine abnormalities, infections, or conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It is advisable to undergo a thorough evaluation, which may include the following hormonal tests: • Luteinizing Hormone (LH) • Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) • Progesterone • Prolactin • Testosterone If you also experience spotting before, during, or after your period, these investigations can help identify the underlying cause. The results should be reviewed and interpreted by a qualified healthcare professional, who will recommend the appropriate management or treatment plan.
WHY YOU ARE STILL TRYING TO CONCIEVE DESPITE ALL GOOD RESULTS

Why some women find it difficult to get pregnant even when they have good results. The result shows that your hormones are balance, your tubes are opened, and your husband semen is very good, yet you are not pregnant. some always think of it as spiritual effect because the professionals failed to explain well to them. It is because majority of the sperm cells during your mid cycle are not getting to your fallopian tubes. Pregnancy occur when the sperm cells meet the fallopian tube and fertilization takes place. Though there is no test to detects if the sperm cells get to the fallopian tubes in your body but there is test to check the cervix level, which is also known as post coital test to confirm if the sperm cells are still active after 24 hours it was released to your body. There are many reasons why sperm may not get to where it will initiate pregnancy: these reasons are cervical hostility, which means the fluid in your cervix is very acidic and it can kill sperm cells when it gets to where it is to fertilize. That is why it is required/important for women to be well romance ad get wet before penetration and release occurred. The wetness is to reduce the acidity in the cervix area. Another reason is when the penis is not long enough to release sperm into the vaginal for it to find its way to the cervix, to the womb and the fallopian tubes. Also, if you have sex using missionary position and you did not feel pain at the mouth of your womb, it means your husband’s penis is not getting to the mouth of the cervix because the sperm may not swim to the fallopian tube. If you are experiencing this, you can change to doggy position for more effectiveness.
YOU CAN HAVE REGUALR MENSTRUAL PERIODS AND NOT OVULATING
Do you know it is possible not to have egg and still be menstruating regularly. Majority believed that it is the unfertilized egg that result to menstruation. But as long as your womb is physically okay, you will always menstruate. When you have hormone that controls menstrual cycle in the body. Is the same with those who have PCOS, and still menstruate. What happen is that when the egg is released from your ovary and after getting to the fallopian tubes and did not see the sperm to fertilized it, will dissolves and be absorbed back to your system. whether you menstruate or not does not concern the egg. It is until you do test and confirm it.
EMOTIONAL STRESS CAN AFFECT GETTING PREGNANT

I want to talk about emotional stress especially in relationships. Emotional stress can affect your hormones, and if your hormones are not well balanced, getting pregnant will be difficult. If your husband is giving you emotional stress. My advice is to ignored whatever is making you down emotionally. Because it may hinder baby from coming. Just overlook and keep calm in expectation of your miracle
