ABUSE OF CLOMID/LETROZOLE CAN LEAD TO OVARIAN CYST.
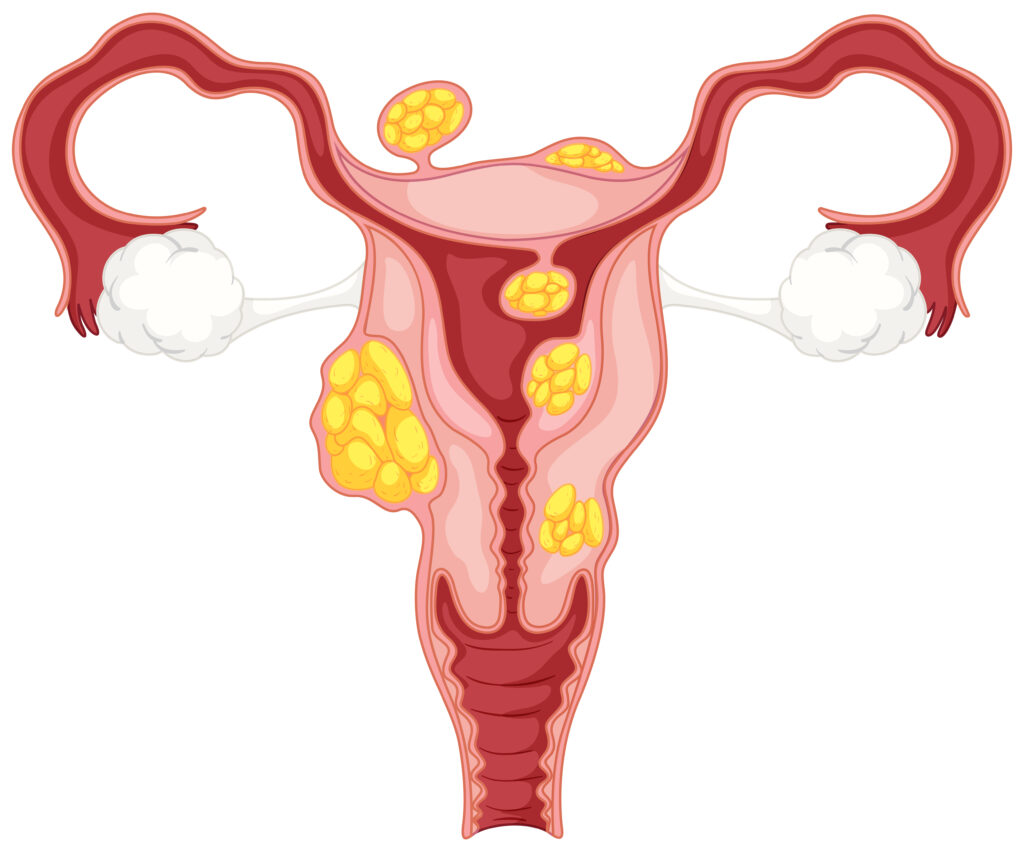
It is important for women trying to conceive to understand that the inappropriate or unsupervised use of ovulation induction medications such as Clomid (clomiphene citrate) and Letrozole can lead to serious complications, including the development of ovarian cysts. In some cases, this has progressed to the extent of requiring surgical intervention. Clomid and Letrozole are both ovulation stimulating agents that should only be taken under the supervision of a qualified fertility specialist. These medications are not meant for casual or experimental use. While some individuals may conceive after using them, others may experience adverse effects, especially if their hormonal profile or ovarian reserve has not been properly evaluated beforehand. Clomid, in particular, can be more aggressive on the ovaries compared to Letrozole. However, neither should be taken without first assessing key fertility parameters such as hormonal balance, ovarian reserve, and the presence of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Using these drugs blindly can overstimulate the ovaries, causing multiple immature follicles to form and increasing the risk of cysts rather than healthy ovulation. It is also concerning to hear that some individuals have been advised to take Clomid and Letrozole simultaneously a practice that is not recommended and may pose a risk to ovarian health. In summary, women waiting on God for the fruit of the womb must seek professional medical evaluation and guidance before initiating any fertility treatment. The health of the ovaries should be protected through careful, informed, and personalized medical care.
Cryptic or Chemical Pregnancy. A fraudulent conception.

Some individuals falsely claim they can help women conceive, even offering to “select” the number of babies for a fee. Victims are given substances to use during intercourse and are later told they are pregnant, with strict warnings to avoid medical scans. These scammers provide false updates, charge for fake tests and herbs, and sometimes manipulate the woman’s body or mind to simulate pregnancy symptoms. In extreme cases, women are called in after nine months, sedated, and later shown a baby—falsely claiming they delivered without remembering labor. Advice to the public: Any center that prevents you from confirming a pregnancy through a certified scan or insists you must deliver only at their facility is fraudulent. Always seek care from licensed medical professionals. Do not fall for emotional manipulation or unverified treatments. Your reproductive health deserves credible, evidence-based care.
Blocked Fallopian Tubes.
For a woman to conceive naturally, at least one fallopian tube must be patent (open and functional). This is because fertilization, when the sperm meets the egg typically occurs within the fallopian tube. If both tubes are blocked, natural conception is not possible, as the sperm and egg cannot meet. Even in cases where assisted reproductive techniques such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) are being considered, tubal patency is essential. One functional tube is required for IUI to be effective. “Patent” in this context means that the tube is unobstructed and allows for the free passage of the egg and sperm. Some women undergo hydrotubation or tubal flushing to attempt to reopen blocked tubes. However, it is important to understand that these procedures do not guarantee restored patency. Clinical experience shows that only a small percentage of women with tubal blockage benefit from these procedures. If conception does not occur within 2 to 3 months after hydrotubation or tubal flushing, it is advisable to repeat tubal patency testing to avoid unnecessary delays in achieving pregnancy. For women considering invitro fertilization (IVF), functional fallopian tubes are not required, as fertilization occurs outside the body in the laboratory. Therefore, women with bilateral tubal blockage may consider IVF as a more effective alternative. In summary, tubal evaluation is a crucial step in fertility assessment. If you have undergone a procedure to unblock your tubes and you are not achieving pregnancy, speak to a fertility scientists.
FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED FOR THE SUCCESS RATE OF IVF.
Many patients ask about the success rate of IVF and expect a guaranteed positive result. However, several medical and biological factors influence IVF outcomes, and success is not automatic. Maternal age is a major determinant. Egg quality declines with age, especially after 35. For women aged 35–40 using their own eggs, the success rate ranges from 40%–50%. Even with donor eggs, the recipient’s age still affects fertility outcomes. Embryo quality is another vital factor. It depends on the genetic and structural integrity of the egg and sperm, whether from the couple or donors. High-grade embryos (Grade A or B) increase the likely hood of success but don’t guarantee implantation. Uterine receptivity is crucial. Even with excellent embryos, the uterus must be receptive for implantation. This is an area where clinical control is limited. Sometimes, a mock embryo transfer is used to assess uterine response. Another factor to considered by the clinic are: 1)Clinic specific patient selection process. This has to do with the rules, guideline or policies. 2)The quality of the sperm and egg should be considered. 3)The treatment method differs. All these can determine the success rate of both the patients and clinic.
FOLLICULAR TRACKING, OVULATION AND AMH.
During follicular tracking, a sonographer may report the presence of 2, 3, or 4 follicles. It is important to understand that these are follicles, not confirmed eggs. The presence of a follicle does not guarantee the presence of a viable egg within. Only during IVF can eggs be retrieved and assessed by an embryologist to determine their number and quality. Egg quality plays a crucial role in fertility and is assessed through a blood test called Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH). An AMH level between 1.0 and 3.5 ng/mL generally suggests a good ovarian reserve and potentially better egg quality. Levels below 1.0 ng/mL may indicate diminished ovarian reserve. If you are trying to conceive, it is advisable to conduct hormonal tests such as AMH, LH (Luteinizing Hormone), and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone). These results should be interpreted by a qualified fertility specialist for accurate guidance and appropriate treatment planning.
WHY YOU ARE NOT RESPONDING TO THE SEMEN TREATMENT.

Persistent low sperm count (oligospermia) or absence of sperm (azoospermia) over time—ranging from 3 months to 2 years, may indicate underlying pathology. Normally, sperm is produced in the testicles and transported via the epididymis through a duct (vas deferens) to mix with seminal fluid from accessory glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral gland) during ejaculation. If sperm count fluctuates or remains at zero despite treatment, there are two main concerns: either the testicles are not producing sperm, or there is an obstruction preventing sperm transport. A common cause of obstruction is a cyst or blockage in the reproductive tract, preventing sperm from reaching the seminal fluid. This results in ejaculated semen lacking sperm cells. Such cases require thorough evaluation by a fertility specialist, including advanced semen analysis, hormone profiling, and possible scrotal or transrectal ultrasound. Seek professional assessment for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
WHEN YOU ARE TRYING TO CONCEIVE AT 40+

Fertility naturally declines with age, and while pregnancy after 40 is possible. It is advisable to aim for conception before age 40. However, if you are trying at 40+, here are key steps to take: 1. Assess Ovarian Reserve: Check your Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) level to evaluate egg quality and quantity. A low AMH may indicate diminished ovarian reserve, making conception more difficult. 2. Evaluate Hormonal Balance: Test Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH). Elevated levels may suggest reduced ovarian function associated with age. 3. Check Tubal Patency: At least one fallopian tube must be open to allow fertilization. An HSG (hysterosalpingography) can assess this. 4. Assess Semen Quality: Ensure the sperm sample is of optimal quality—both count and motility are essential. Understanding and addressing these factors early can improve your chances of a successful pregnancy. Always consult a fertility specialist for guided support.
IF YOU ARE A VIRGIN OR NOT SEXUALLY ACTIVE. THESE SIGNS ARE NOT GOOD.

This message is directed to women who have never been sexually active or are virgins prior to marriage. It is important to understand that virginity is not an indicator of fertility. The assumption by some that marrying a virgin guarantees fertility is medically incorrect. Fertility is determined by several physiological and hormonal factors not by sexual history. In fact, certain symptoms experienced even in the absence of sexual activity may signal underlying reproductive health issues. For instance, if a woman has irregular or absent menstrual cycles, it may be a sign of hormonal imbalance or conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). These issues, if not identified and addressed early, can impact her ability to conceive later in life. Other signs that should not be ignored include cyclic breast tenderness (swelling before menstruation that resolves afterward) or a lack of sexual arousal, which may be linked to hormonal insufficiencies or endocrine disorders. Regardless of sexual activity, any woman experiencing these symptoms should consult a fertility scientists for proper evaluation. Early detection and management of reproductive health issues are key to preserving fertility, even in women who remain virgins until marriage.
IS IT TRUE THAT SPERM CELLS STAYS 3 DAYS IN THE VARGINA?
There is a common misconception that sperm cells can survive for up to three days within the female reproductive tract. While this is sometimes possible, it is not a guarantee and it depends on several biological factors. Firstly, the cervical mucus plays a critical role. This fluid, produced at the cervix (the opening of the uterus), varies in composition throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. During the fertile window, cervical mucus becomes less acidic and more conducive to sperm survival, creating a pathway for sperm to swim toward the egg. Outside this window, however, the cervical environment can be hostile, and sperm may be destroyed almost immediately after ejaculation. Secondly, the quality of the sperm itself is essential. Sperm with poor motility (sluggish movement) or abnormal morphology may fail to reach the cervical canal or may not survive long enough to fertilize an egg. Additionally, the integrity of the sperm DNA is another critical factor that can affect viability. Therefore, if ovulation is expected on a specific day say, it is not advisable to rely solely on intercourse three days prior, assuming that sperm will survive until then. For the highest chance of conception, it is recommended to have intercourse on the day of ovulation or within the fertile window as guided by ovulation tracking. In summary, while sperm cells can survive up to five days in optimal conditions, this is not always the case. Factors such as cervical mucus quality, sperm health, and timing all play significant roles in determining the likely hood of conception.
Can Ovarian Reserve Be Restored at Age 40?
It is important to understand the biological changes that occur in female fertility, especially for women aged 40 and above who are trying to conceive. Ovarian reserve naturally declines with age, and this decline becomes more significant after the age of 35. At age 40 and above, evaluating key hormonal markers such as Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinizing Hormone (LH), and Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) are crucial. If your FSH and LH levels fall within the normal range (typically between 4–10 IU/L), and your AMH is low, the use of fertility-enhancing supplements may offer some benefit. In some cases, with proper support and supplementation, there can be a mild improvement in ovarian function. However, if LH levels are elevated and AMH is significantly low, especially in women over 40, restoring ovarian reserve becomes much more challenging. This is why it’s essential to undergo proper diagnostic testing before starting any fertility supplement, including products like Fertilgain, which are designed to support ovarian function. In women with diminished ovarian reserve, abnormal FSH and LH levels can also disrupt menstrual regularity, further complicating conception efforts. Key recommendation: Any woman attempting to conceive, particularly at 40 years and above, should undergo an AMH test as part of their fertility assessment. It provides valuable insight into the quantity of remaining eggs and overall ovarian reserve, thereby guiding appropriate medical or supportive interventions.
